Bilateral hearing loss

What is bilateral hearing loss?
Hearing loss that affects both ears is referred to as bilateral hearing loss. While it is common for bilateral hearing loss to occur gradually over time, in some (rare) cases, it can occur suddenly.
Since the experience of bilateral hearing loss can vary from one person to another, it is important to have your hearing loss evaluated by a hearing care expert. Additionally, there are other hearing health conditions that might have overlapping symptoms with bilateral hearing loss, so seeking advice from an expert will ensure that you are treated for your specific hearing loss needs.
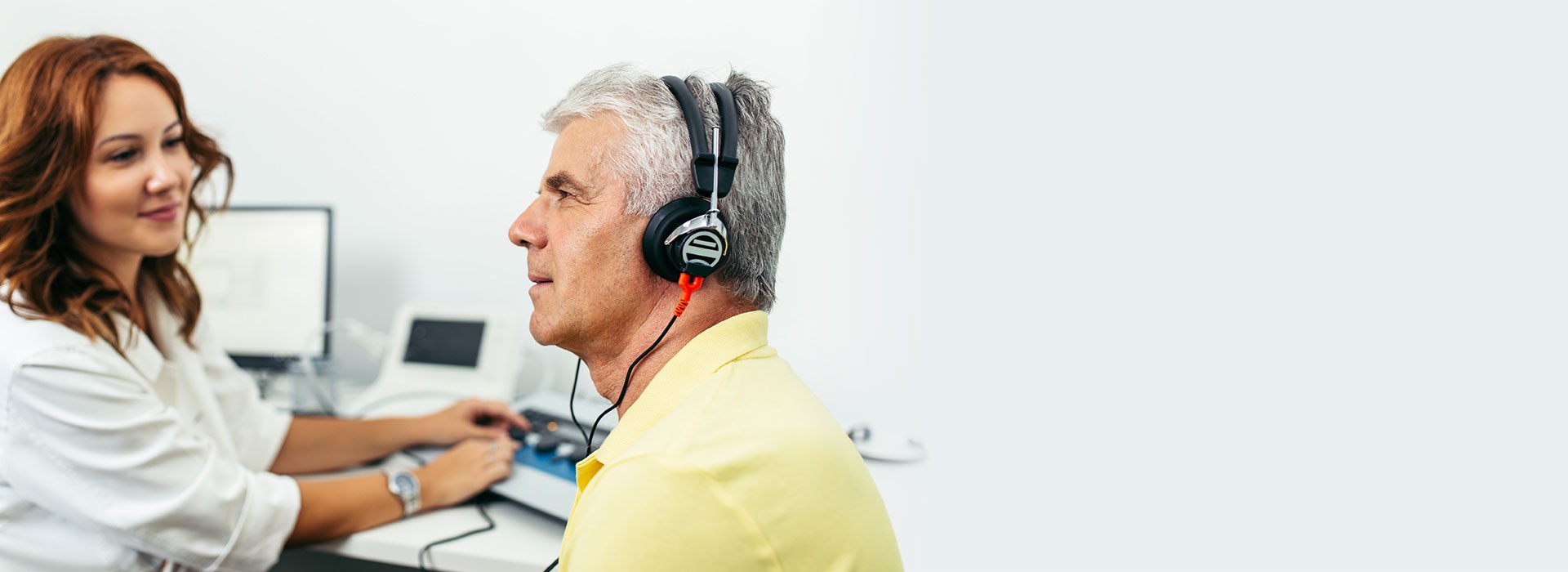


Book a free test for bilateral hearing loss
What causes bilateral hearing loss?
Learn about the various factors that can cause hearing loss:
Symptoms of bilateral hearing loss
Since hearing loss often occurs gradually over time, it can be difficult to identify the symptoms. Whether the signs of hearing loss are obvious or not, it is worth seeking professional advice even if you only notice the slightest of signs. Being proactive will help you to receive a proper diagnosis as early as possible so that you can seek treatment (if necessary). Any recognisable symptoms can be a sign of mild, moderate, severe, or profound hearing loss.
Common symptoms of hearing loss include:
- Difficulty understanding others, especially in noisy environments.
- Turning up the TV volume louder than usual.
- Asking others to repeat themselves.
- Relying on lip reading to understand what others are saying.
Additionally, unilateral hearing loss is typically easier to spot since sounds will be louder in one ear than the other. Bilateral hearing loss can be identified when sound is generally more difficult to hear in both ears.

Treatment for bilateral hearing loss
Modern hearing aids are able to provide those with bilateral hearing loss with a natural hearing experience. Today's hearing aids not only amplify sound, but they send detailed sound signals to the brain, so that you can hear better with less effort.
In fact, the latest hearing aids can significantly improve speech understanding and increase the amount of sound delivered to the brain, providing a clearer sound scene. This enables those with bilateral hearing loss to hear more details in surrounding sounds.
Types of bilateral hearing loss
Bilateral hearing loss can be classified as either sensorineural or conductive in nature.
Bilateral sensorineural hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss implies that the tiny hair cells in the inner ear or the auditory nerve (responsible for transmitting sound to the brain) are damaged. It is most often caused by the natural aging process or exposure to loud sounds.
Sensorineural hearing loss
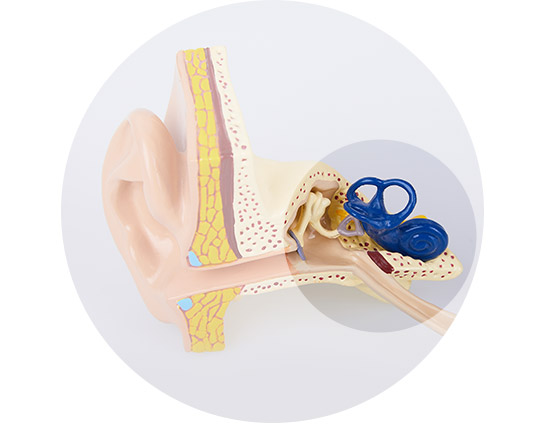
Bilateral conductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs in the outer or middle part of the ear, where sound is converted to vibrations and sent to the inner ear. This type of hearing loss refers to issues with transferring sound waves (due to a blockage or other impediment.) Excessive earwax, a ruptured ear drum, or even ear infections can result in conductive hearing loss.
Conductive hearing loss

Sources
1. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanam/article/PIIS2667-193X(23)00244-2/fulltext
2. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14992027.2022.2119611
3. https://journals.lww.com/ear-hearing/abstract/2022/05000/a_predictive_model_of_bilateral_sensorineural.33.aspx
4. https://pathsocjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/path.2102